New TECH Report - ABS/SAN Resins (2025 Program)
ABS/SAN Resins is one in a series of reports published as part of NexantECA’s 2025 Technoeconomics – Energy & Chemicals (TECH) program
Overview
The first commercial grades of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) polymer, originally introduced in 1948, were simply mechanical blends of rubber with styrene acrylonitrile (SAN) polymer. Today, ABS polymers are composed of elastomer dispersed as a grafted particulate phase in a thermoplastic matrix of SAN. ABS polymers are tough and thermally resistant with butadiene contributing toughness and low temperature impact strength, acrylonitrile improving thermal stability and chemical resistance, and styrene lending rigidity to the composition. The ABS polymer system, though structurally complex, offers unique advantages in tailoring properties to meet specific product needs and allows for a wide range of versatility.
This TECH report discusses the common production routes to ABS, including emulsion, mass, and hybrid processes, and addresses the following questions:
What process technologies are used to produce ABS resins and how do they differ?
Which production routes are most prevalent today and why?
How do the properties of ABS resins change with composition and what are typical ABS resin compositions?
What are the new technology developments in this area and what benefits do they bring compared to current ABS production?
Which process route is the most cost competitive and what are key cost drivers?
Technologies & Configurations Overview
The common production routes to ABS include emulsion, mass, and hybrid processes. While the production of ABS by the emulsion process is rarely used commercially today, it is discussed in the report as a basis for the hybrid emulsion/mass process that is commercially prevalent. Compounding of a high graft rubber ABS and SAN is also discussed.
Process Economics
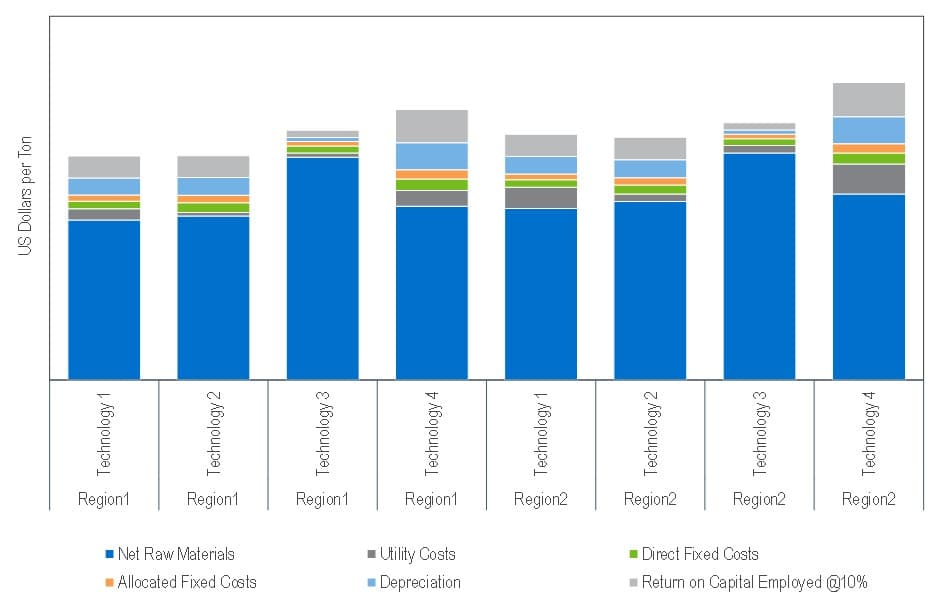
Process economics for the various technologies used for the production ABS are presented for the United States, Western Europe, and China
Example of Process Economics Analysis for Various ABS Production Process
Commercial Overview
Asia Pacific is the largest producing region, with over 85 percent of global ABS capacity. Growth in ABS capacity in the Asia Pacific region followed ABS consumption patterns which increased dramatically in the region with the underlying shift in manufacturing to lower-cost areas such as China.
Demand drivers for ABS include its flexibility of composition and structure which allows it to exhibit a wide range of properties and thus be used in diverse applications such as electronics, appliances, transportation (automotive), and consumer pipes and fittings. Despite this, global ABS demand has recently been under pressure from inter-polymer competition, especially from polypropylene in automotive and other applications requiring a medium range of properties.
Contact a member to our Insights & Analytics team to find out more about this report